views
Waste-to-Energy Market: A Sustainable Solution for a Greener Future
The global Waste-To-Energy (WtE) Market Share is emerging as a critical player in the fight against climate change and resource depletion. As the world grapples with mounting waste generation and the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, waste-to-energy technologies offer a promising pathway to address both challenges simultaneously. By converting waste into usable energy, these technologies not only reduce the burden on landfills but also contribute to the global energy mix. This article delves into the waste-to-energy market, exploring its definition, growth drivers, segmentation, country-level analysis, and competitive landscape, while emphasizing its human and environmental impact.
Market Estimation & Definition
The waste-to-energy market refers to the process of generating energy—typically electricity or heat—from the treatment of waste materials. This is achieved through various technologies such as incineration, gasification, pyrolysis, and anaerobic digestion. The energy produced can be used to power homes, industries, and even vehicles, making it a versatile and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
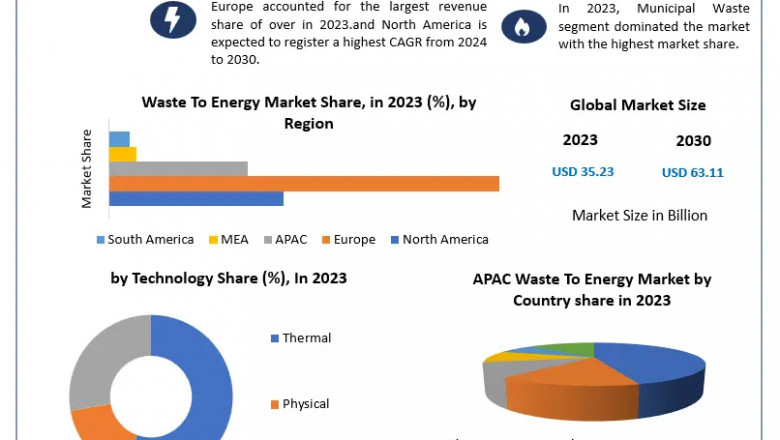
According to Maximize Market Research, the global waste-to-energy market was valued at USD 35.10 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2029, reaching approximately USD 58.21 billion by 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, rising waste generation, and the global shift toward renewable energy sources.
At its core, waste-to-energy is not just about generating power; it’s about reimagining waste as a resource. Every ton of waste processed through WtE technologies reduces greenhouse gas emissions, minimizes landfill use, and contributes to a circular economy. For communities worldwide, this means cleaner cities, reduced environmental pollution, and a step closer to achieving sustainability goals.
Click Here For Free Sample Report Link:https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/13394/
Market Growth Drivers & Opportunities
The waste-to-energy market is driven by a combination of environmental, economic, and social factors. Here are the key drivers shaping its growth:
-
Rising Waste Generation: Urbanization and population growth have led to an exponential increase in waste generation. According to the World Bank, global waste is expected to grow by 70% by 2050 if current trends continue. Waste-to-energy technologies provide a viable solution to manage this waste while generating energy.
-
Government Policies and Incentives: Governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations to reduce landfill use and promote renewable energy. For instance, the European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan and the U.S. Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) are driving investments in WtE projects.
-
Energy Security Concerns: With the volatility of fossil fuel prices and the geopolitical tensions surrounding energy resources, countries are increasingly looking for domestic and sustainable energy sources. Waste-to-energy offers a reliable and locally available energy option.
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations in WtE technologies, such as advanced gasification and plasma arc gasification, are improving efficiency and reducing emissions. These advancements are making WtE more economically viable and environmentally friendly.
-
Public Awareness and Corporate Responsibility: Growing awareness about environmental issues and the role of waste management in sustainability is encouraging both individuals and corporations to adopt greener practices. Companies are investing in WtE solutions as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
The opportunities in the waste-to-energy market are vast. Emerging economies, in particular, present untapped potential due to their rapid urbanization and inadequate waste management infrastructure. Additionally, the integration of WtE with other renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind, could create hybrid energy solutions that further enhance sustainability.
Segmentation Analysis
The waste-to-energy market can be segmented based on technology and waste type. Understanding these segments provides a clearer picture of the market dynamics.
-
By Technology:
-
Incineration: The most widely used WtE technology, incineration involves burning waste at high temperatures to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. It is favored for its ability to handle large volumes of waste.
-
Gasification: This process converts waste into synthetic gas (syngas) by reacting it at high temperatures with a controlled amount of oxygen. Syngas can be used to produce electricity or as a chemical feedstock.
-
Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis involves heating waste in the absence of oxygen to produce bio-oil, syngas, and char. It is particularly effective for processing plastic waste.
-
Anaerobic Digestion: This biological process breaks down organic waste in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas, which can be used for electricity or heat generation.
-
-
By Waste Type:
-
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): Household and commercial waste is the primary feedstock for WtE plants.
-
Industrial Waste: Waste from manufacturing and industrial processes is increasingly being used in WtE systems.
-
Biomedical Waste: Specialized WtE technologies are being developed to safely process hazardous biomedical waste.
-
Each segment has its unique challenges and opportunities. For instance, while incineration dominates the market, gasification and pyrolysis are gaining traction due to their lower emissions and higher efficiency.
More Insights Of Full Report In Details:https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/waste-to-energy-market-wte/13394/
Country-Level Analysis
The adoption and growth of waste-to-energy technologies vary significantly across countries, influenced by regulatory frameworks, waste management practices, and energy needs.
-
United States: The U.S. is a leading player in the WtE market, driven by its large waste generation and supportive policies. The country has over 70 WtE plants, primarily using incineration technology. States like Florida, New York, and Massachusetts are at the forefront of WtE adoption. The U.S. government’s focus on reducing landfill use and achieving renewable energy targets is expected to further boost the market.
-
Germany: As a pioneer in environmental sustainability, Germany has been a key adopter of waste-to-energy technologies. The country’s Energiewende (energy transition) policy emphasizes the shift from fossil fuels to renewables, including WtE. Germany’s advanced incineration and anaerobic digestion plants serve as models for other countries.
-
Emerging Economies: Countries like India, China, and Brazil are witnessing rapid growth in their WtE markets. For instance, China’s “Zero Waste Cities” initiative aims to improve waste management and increase WtE capacity. India, with its Swachh Bharat Mission, is also investing in WtE projects to address its waste crisis and energy deficit.
Competitive Analysis
The waste-to-energy market is highly competitive, with key players focusing on innovation, partnerships, and expansion to gain a competitive edge. Some of the leading companies in the market include:
-
Covanta Holding Corporation: A U.S.-based company specializing in waste-to-energy and waste management services.
-
Veolia Environnement: A French multinational offering comprehensive WtE solutions, including incineration and anaerobic digestion.
-
Suez SA: Another French company known for its advanced waste management and energy recovery technologies.
-
Hitachi Zosen Corporation: A Japanese firm with a strong presence in the global WtE market, offering cutting-edge incineration and gasification technologies.
These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve the efficiency and sustainability of their technologies. Strategic partnerships with governments and private entities are also driving market growth.
Conclusion
The waste-to-energy market represents a transformative approach to waste management and energy production. By turning waste into a valuable resource, WtE technologies are addressing two of the most pressing challenges of our time: waste management and energy security. As governments, corporations, and individuals increasingly recognize the importance of sustainability, the WtE market is poised for significant growth.
However, the success of this market depends on continued innovation, supportive policies, and public awareness. While challenges such as high initial costs and environmental concerns remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. Waste-to-energy is not just a market opportunity; it’s a pathway to a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future for all.
As we move forward, the waste-to-energy market will play a pivotal role in shaping the global energy landscape. By embracing this technology, we can turn the tide on waste and energy challenges, creating a world where nothing goes to waste—literally.













Comments
0 comment