views
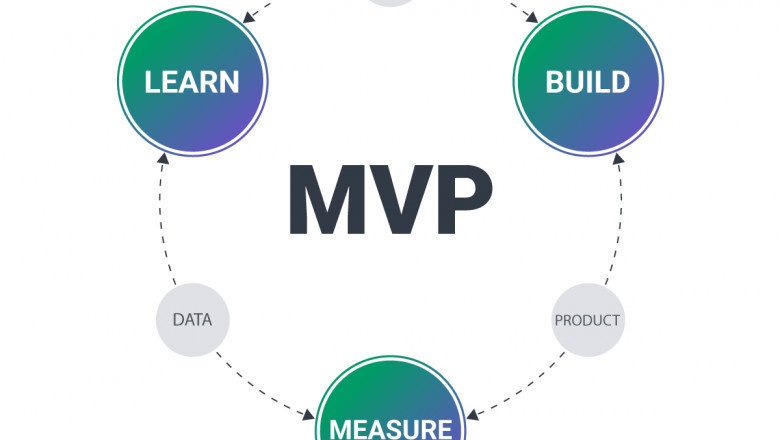
In the fast-paced world of startups and software development, launching a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a crucial step in validating an idea before full-scale development. MVP development services help businesses create a functional product with essential features, allowing them to gather user feedback and make improvements. In this article, we’ll break down the key phases of MVP development services to help you understand the process and its importance.
Phase 1: Idea Validation
Before developing an MVP, it’s essential to validate the business idea. This phase ensures that the product concept aligns with market demands and solves a real problem.
Steps in Idea Validation:
-
Market Research: Analyze competitors and identify gaps in the industry.
-
Target Audience Analysis: Define the ideal users and their pain points.
-
Value Proposition: Clearly outline the problem your product solves.
-
Feedback Collection: Conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gauge interest.
A well-validated idea reduces risks and increases the chances of building a successful MVP.
Phase 2: Defining Core Features
Once the idea is validated, the next step is identifying the core features that define the MVP. The goal is to include only essential functionalities that address the primary problem without unnecessary complexity.
Steps in Feature Definition:
-
Prioritize Features: List all potential features and categorize them as ‘must-have’ or ‘nice-to-have.’
-
User Journey Mapping: Outline the customer’s interaction with the product.
-
Wireframing & Prototyping: Create basic visual representations to understand the user flow.
By focusing on core features, businesses can launch the MVP faster and iterate based on user feedback.
Phase 3: MVP Development
With a clear feature set, development begins. The objective is to build a working product that delivers value with minimal resources.
Key Aspects of MVP Development:
-
Technology Stack Selection: Choose the appropriate tools, frameworks, and platforms.
-
Agile Development Approach: Break down development into sprints to ensure efficiency.
-
UI/UX Design: Create a simple, intuitive, and user-friendly interface.
-
Back-End Development: Implement database structures and APIs.
-
Front-End Development: Build a functional interface for user interaction.
At the end of this phase, the MVP should be a fully operational product with limited but essential functionality.
Phase 4: Testing & Quality Assurance
Before launching the MVP, rigorous testing is necessary to ensure a smooth user experience.
Types of Testing:
-
Functional Testing: Verifies that all features work correctly.
-
Usability Testing: Assesses the product’s ease of use.
-
Performance Testing: Measures speed and responsiveness under various conditions.
-
Bug Fixing: Identifies and resolves issues to improve stability.
This phase helps minimize potential problems, ensuring that the MVP is ready for real users.
Phase 5: Launch & User Feedback
Once testing is complete, the MVP is ready for launch. The goal is to release the product to a small user group to gather insights and measure performance.
Key Steps During Launch:
-
Soft Launch or Beta Testing: Introduce the product to a select audience.
-
Marketing & Promotion: Use digital marketing strategies to attract early adopters.
-
Monitor User Behavior: Analyze engagement, retention rates, and user interactions.
-
Collect Feedback: Gather insights through surveys, reviews, and analytics.
Early user feedback helps determine if the product meets expectations or requires adjustments.
Phase 6: Iteration & Improvement
After launch, continuous improvement is necessary to enhance the MVP based on user feedback.
Iteration Strategies:
-
Identify Patterns: Look for recurring feedback and prioritize changes.
-
Feature Enhancements: Add or refine features based on demand.
-
Fix Issues: Resolve reported bugs and usability concerns.
-
Scale the Product: Expand functionalities and infrastructure as the user base grows.
Iteration ensures that the MVP evolves into a polished product ready for wider adoption.
Conclusion
By focusing on essential features and gathering real-world feedback, companies can refine their products before investing heavily in full-scale development. Following these key phases ensures a successful MVP launch and paves the way for future growth and innovation.
Read More:https://www.wpwhales.io/













Comments
0 comment